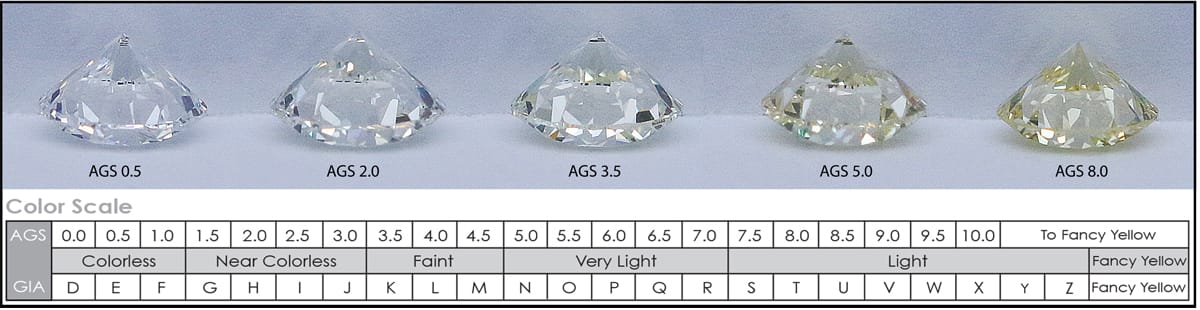
Diamond Color Grading Chart According To GIA Standards.
Diamond color is all about what you can’t see. Diamonds are valued by how closely they approach colorlessness – the less color, the higher their value. (The exception to this is fancy color diamonds, such as pinks and blues, which lie outside this color range.) Most diamonds found in jewelry stores run from colorless to near-colorless, with slight hints of yellow or brown.GIA’s color-grading scale for diamonds is the industry standard. The scale begins with the letter D, representing colorless, and continues with increasing presence of color to the letter Z, or light yellow or brown. Each letter grade has a clearly defined range of color appearance. Diamonds are color-graded by comparing them to stones of known color under controlled lighting and precise viewing conditions.Many of these color distinctions are so subtle as to be invisible to the untrained eye. But these slight differences make a very big difference in diamond quality and price.
Why Does The GIA Color Grading System Start At D?
Before GIA developed the D-Z Color Grading Scale, a variety of other systems were loosely applied. These included letters of the alphabet (A, B and C, with multiple A’s for the best stones), Arabic (0, 1, 2, 3) and Roman (I, II, III) numerals, and descriptions such as “gem blue” or “blue white.” The result of all these grading systems was inconsistency and inaccuracy. The creators of the GIA Color Scale wanted to start fresh, without any association with earlier systems, they chose to start with the letter D—a letter grade normally not associated with top quality. Actual colors on scale D to Z for White to Yellowish Diamonds
each diamond has its own color and will differ from the standard color. Notice that nature did not trace lines between the gradually passage of the colors. Presence of a yellowish tint, lowers the price of Diamond